Spatial Computing For Enterprise
Reimagining Healthcare: How AI and Spatial Computing Are Redefining Patient Care
"The integration of data and technology is fundamentally changing how we approach medicine. By harnessing the power of genomics, wearables, and predictive analytics, we can move from a one-size-fits-all model to truly personalized care, tailored to the unique genetic makeup and lifestyle of each patient." - Dr. Eric Topol, Cardiologist and Author of The Patient Will See You Now
The first wave of AI and spatial computing is already flowing through Singapore’s hospitals, setting new baselines for what’s possible in care. At Tan Tock Seng and the National University Health System, machine intelligence scans X-rays, MRIs, and patient records with a scale and speed no clinician alone could match. Diagnoses arrive faster, more consistently, with new patterns caught in the digital net, giving doctors sharper eyes and patients quicker answers.
Meanwhile, Singapore's Health Promotion Board pilots programs that hand every participant a new kind of companion: wearable devices quietly streaming real-time vitals, watching for subtle signs of health decline in daily life. Early warnings once invisible now spark timely intervention. Alongside these, digital health coaches provide lifestyle management and preventive care, nudging habits and creating accountability tailored to each user’s data patterns.
These experiments represent a fundamental rethink of healthcare as persistent, personalized, and predictive rather than episodic and reactive. Each step connects more dots, giving patients and professionals tools to stay ahead of illness rather than merely catch up when it strikes.
AI-powered 3D Imaging and Spatial Interactions
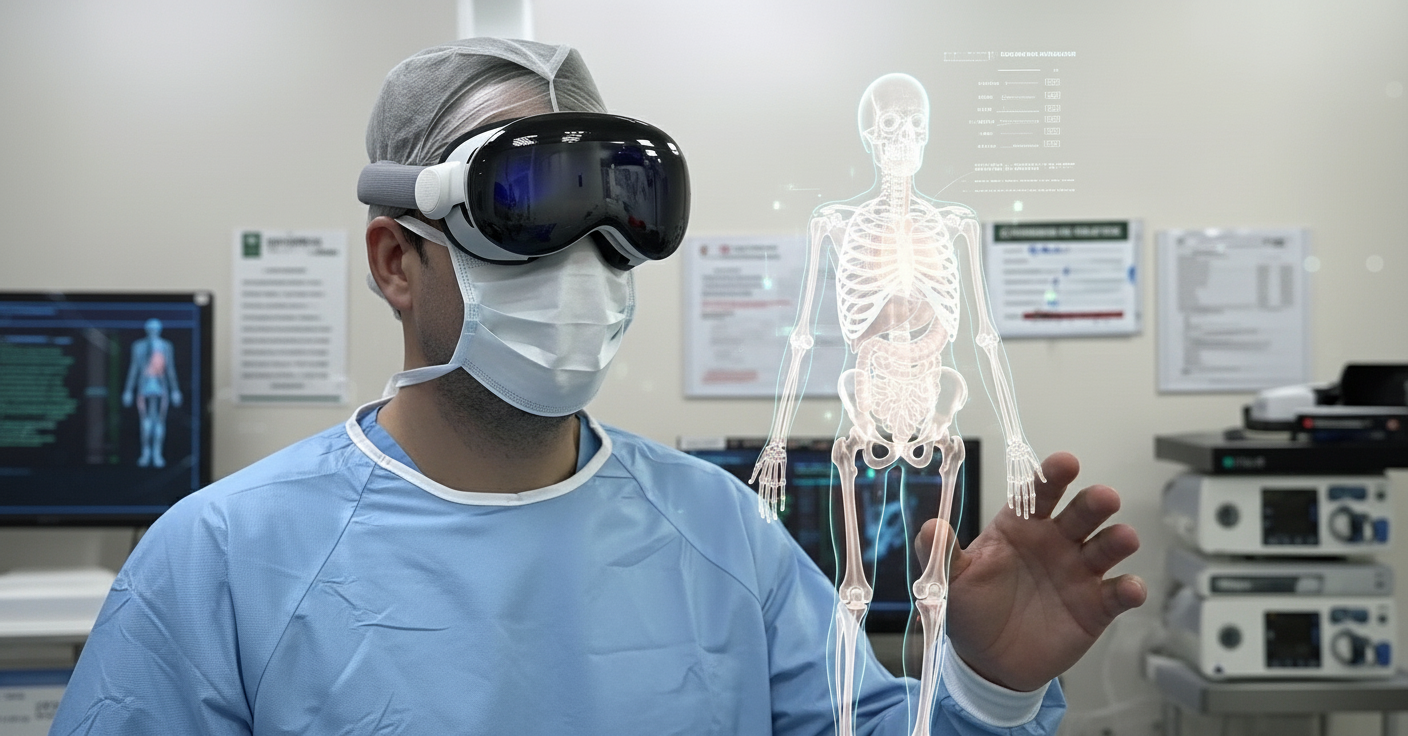
AI-driven 3D imaging is reshaping diagnostics, transforming how doctors see, plan, and deliver care. Instead of generic, population-based models, clinicians now work with detailed, patient-specific anatomy. Detailed, lifelike visualizations improve diagnosis and treatment planning. This leap in precision enables personalized surgeries, custom prosthetics, and digital twins for real-time simulation and optimization. Image enhancement algorithms are cutting MRI scan times from an hour to just ten minutes, streamlining workflows and vastly improving the patient experience.
Spatial computing brings all this data, scans and vast medical information, to life. It creates immersive, interactive environments where clinicians and patients explore complex anatomical structures in real time through smart glasses or VR headsets. By overlaying digital models onto the patient’s body, it enhances both diagnostic clarity and surgical precision.
Overcoming the Digital Divide for Patients and Providers
Beyond individual care, spatial computing enables remote collaboration, allowing specialists in different locations to interact with the same 3D models. This expands access to expertise and deepens understanding during consultations. Innovations like pocket-sized ultrasound devices, for example Vscan, provide high-resolution imaging of organs like the heart at the bedside, saving time and cost, around $1,500 per echo. Patients can also share spatially accurate images using photogrammetry and depth scanning, even from smartphones, making remote submissions possible. This democratizes expert care and speeds diagnosis and treatment.
3D and spatial scans enable physicians to highlight key problem areas in rich visual detail, boosting communication and empowering patients, especially when interpreting complex findings.
Digital Innovation In Healthcare Services
Current technology capabilities open new pathways for digital innovation in healthcare services. Mobile apps with photogrammetry, 3D, and spatial scanning enable patients with minor concerns to send images for initial screening without visiting a medical facility. These images can be processed by AI trained on vast medical data sets, generating recommendations that follow a quick doctor’s approval. Delivered at low cost, these services let individuals access validated medical advice early, preventing late discovery of issues.
If a scan reveals a concern, the app can also facilitate appointment bookings, streamlining the process and reducing administrative overhead. This fusion of spatial tech and AI creates a new front door to healthcare that is more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered.
Bringing Specialist Expertise to the Frontline
Augmented reality is transforming healthcare collaboration by removing travel barriers and speeding medical responses. Picture a nurse at a community care center tending to an elderly patient with complex needs. She puts on an AR headset like the Apple Vision Pro and instantly connects with a specialist miles away. The doctor appears as a lifelike avatar, sharing her real-time view, creating a powerful sense of telepresence as if physically present.
The doctor uses digital annotations to circle areas of concern on the patient’s skin or highlight readings on monitors, all within the nurse’s field of vision. Pre-recorded spatial videos provide step-by-step guidance for detailed diagnostic procedures, such as joint mobility or neurological assessments, while the doctor supervises.
This real-time connection sharpens diagnostics, enables swift intervention, and turns distance into immediacy. It amplifies expertise and helps frontline caregivers meet rising demands with smarter, faster collaboration.
A New Dimension in Learning and Practice
Medical education is stepping beyond 2D images into fully immersive 3D worlds. A student can now slip on a VR headset and literally walk through a beating heart or navigate the complex highways of the nervous system. Spatial computing transforms learning into an interactive, intuitive experience, one that is easier to grasp, less stressful to acquire, and far stickier in memory.
This shift extends to mastering skills. Surgeons, from rookies to veterans, can rehearse complex procedures repeatedly in hyper-realistic virtual environments with zero risk. This freedom to practice builds deep confidence and competence, quieting the anxiety that so often shadows high-stakes care.
Fostering Empathy and Real-Time Support
Burnout is more than workload. It’s emotional fatigue. VR-based empathy training lets clinicians step directly into a patient’s experience, seeing the world through their eyes, whether that’s vision loss or auditory hallucinations. This first-person perspective fosters deeper empathy, smoothing communication and easing emotional strain in care.
Support also arrives during care itself. AR becomes a second set of eyes, quietly projecting next steps, readings, and expert insights exactly where they’re needed. This real-time overlay of vital data becomes a powerful safety net, helping healthcare professionals act faster and with greater confidence, backed by remote expertise and rich data. By making knowledge instantly accessible and practice less perilous, these emerging tools are building a healthcare workforce that is smarter, more resilient, and less burned out.
Building the Foundation for Digital Medicine
To unlock digital medicine’s full potential, healthcare facilities must start with a scalable, secure infrastructure. This is not just an IT upgrade; it’s the creation of an agile backbone designed to evolve with emerging technologies, shifting patient volumes, and unforeseen crises. Without this flexible framework, even the most advanced AI tools and digital workflows risk becoming isolated pilots instead of integrated, system-wide solutions.
A Future Built on Human-Centered Innovation
adoption but a profound reshaping of how we heal, care, and connect. The most successful systems will weave high-tech efficiency with deep human empathy. They will invest in immersive training to cultivate confident clinicians, empower staff with AI co-pilots, and unlock human-machine collaboration to tackle complex challenges. By keeping the human spark at the center of innovation, we create a healthcare future that is not only bold and resilient but fundamentally human-centered.
The question is no longer whether we can build a more human-centered healthcare system, but whether we will choose to.
Resources
Emrich, T. (2024). The next dimension: How to use augmented reality for. John Wiley & Sons.
Topol, E. (2015). The patient will see you now: The future of medicine is in your hands. Basic Books.
Healthcare Asia. (2023, January 25). Tan Tock Seng Hospital develops virtual reality for staff training. Healthcare Asia Magazine. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://healthcareasiamagazine.com/healthcare/exclusive/tan-tock-seng-hospital-develops-virtual-reality-staff-training
Agency for Integrated Care. (n.d.). Community care digital transformation plan. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://www.aic.sg/partners/community-care-digital-transformation-plan/
Ministry of Health, Ministry of National Development, & Ministry of Transport. (n.d.). About Age Well SG. Age Well SG. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://www.agewellsg.gov.sg/about/
Woon, W. (2022, November 1). New initiative to monitor health of seniors remotely, ensuring timely care and support. The Straits Times. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/community/new-initiative-to-monitor-health-of-seniors-remotely-ensuring-timely-care-and-support
Mitchell, S. (2023, March 24). St Luke’s Eldercare adopts AI-driven network for growth & care. IT Brief Asia. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://itbrief.asia/story/st-luke-s-eldercare-adopts-ai-driven-network-for-growth-care
Tan Tock Seng Hospital. (2022, May 17). Smart wards: Singapore hospitals use technology to cope with manpower needs. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://www.ttsh.com.sg/About-TTSH/TTSH-News/Pages/Smart-wards-Singapore-hospitals-use-technology-to-cope-with-manpower-needs.aspx
