
The landscape of images is rapidly evolving. Visuals are no longer confined to flat JPEGs or looping MP4s pasted onto glowing rectangles. Today, images are swelling into volumes: contoured, layered, alive in space. Screens aren’t merely transparent panes; they've become portals, merging our physical presence with sprawling digital overlays. The image is transforming from a captured window to a lived environment.
The march towards spatial computing, spanning VR, AR, and XR, is surging forward. Industry giants like Apple, Meta, Google, and Xiaomi are not just pushing boundaries, they’re reimagining what’s possible. Apple’s Vision Pro, Xiaomi’s Mijia Glasses Camera, and Meta and Google’s ambitious smart glasses initiatives aren’t just incremental upgrades. They’re keys to a “mirror world”, a dynamic three-dimensional information layer draped atop physical reality.
As spatial tools reshape how we interface with the digital world, a new imperative emerges. We must learn the grammar of immersive visuals: spatial photography, 360° imagery, and 180° video. Each format comes with its own logic, language, and potential.
Spatial photos and videos unlock true presence, allowing users to look around and inhabit a moment as if they’re actually there.
360-degree photos and videos envelop viewers, granting agency to explore scenes by turning their heads or moving their bodies.
180-degree immersive video strikes a balance, focusing attention forward while still providing depth and immersion.
Understanding these formats isn’t about chasing trends. It’s about aligning intention with opportunity. In this article, we will break down the key forms of immersive visual media, not as a manual, but as a guide for brand builders, team leaders, and storytellers, on how to wield the immersive formats reshaping our future.
Spatial Photography & Videography: A Window into Memory
Spatial photography and videography bring a new depth and presence to how we capture and relive moments. This isn't about full VR immersion; it's something subtler: a window into a memory. With the Apple Vision Pro, spatial video shifts from flat rectangles to dimensional scenes, bending subtly with your gaze.
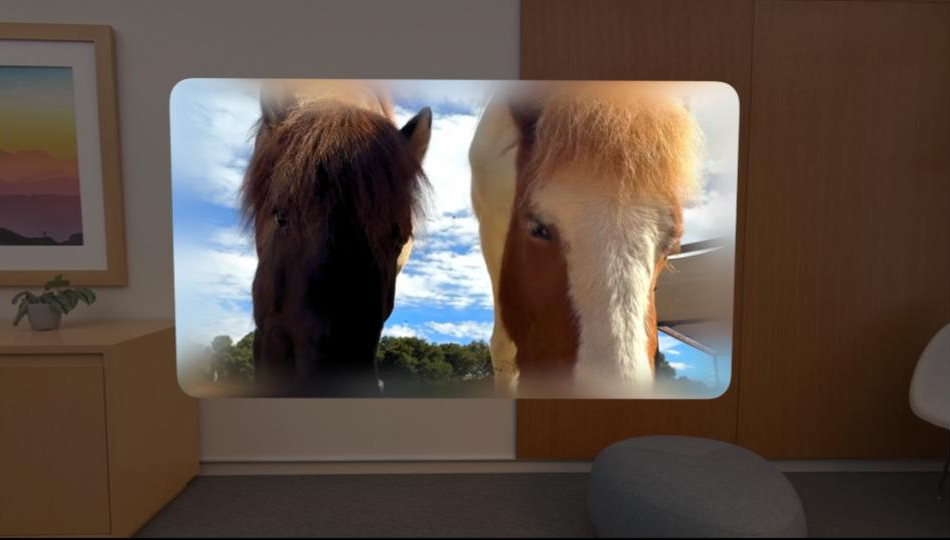

This effect relies on stereoscopy, mimicking our binocular vision, by capturing two slightly different perspectives with dual cameras or lenses, one for each eye. These streams are woven into a single file using Multiview High-Efficiency Video Coding (MV-HEVC). This advanced compression delivers rich, three-dimensional experiences without bloated file sizes.
You can capture spatial photos and videos on an iPhone 15 Pro or newer. A key strength of this format is its backward compatibility: on regular screens, spatial media plays as conventional 2D, but slip on the Vision Pro headset, and these images unfold with authentic depth, letting you inhabit a frozen moment in time.
Harnessing Spatial Media to Build Experiences
Supplementing existing 2D media with spatial photos and videos is a powerful strategy for enhancing user experiences without requiring a complete overhaul of current applications. It adds an immersive layer where it matters most, giving richer context and inviting deeper sensory connection.
Spatial media shines in detailed product showcases that reveal texture and form, in brand stories that resonate emotionally, and in training scenarios where fine, depth-dependent gestures are crucial.
In manufacturing, spatial snapshots turn factory floors into richly detailed, dimensional records of machinery and layouts. They help maintenance teams diagnose issues, troubleshoot, and plan upgrades with clarity flat images lack. Inspecting delicate parts remotely gains new precision through this heightened sense of scale and detail.
In healthcare, spatial photos transform communication. Doctors reviewing spatial photos of wounds or skin conditions captured remotely by patients with a truer sense of depth and context, making remote diagnosis more accurate and empathetic.
On construction sites, spatial videography creates immersive progress records. Site managers capture every phase with layered detail that spotlights issues and ensures compliance.
The true power of spatial media lies not just in its realism, but in its ability to improve decision-making, recall, and emotional connection.
While spatial media offers a focused, personal window into a memory, some scenarios require a more expansive view. This is where 360-degree media comes into play.
360-Degree Photo & Video: The All-Encompassing Environment
360-degree media unfolds a full spherical panorama from a single point of view. It doesn’t frame a fixed scene. Instead, it captures everything all around you, above and below, inviting you to explore at will. This format gives you the freedom to turn your gaze and truly feel transported inside a place.
Capturing 360-degree media involves using cameras with multiple lenses positioned around the camera body to cover every angle simultaneously. Each lens captures a wide-angle shot, and then computational algorithms carefully stitch these visuals together by matching overlapping edges.
One of 360-degree media’s greatest strengths is its accessibility. No special gear is needed to explore these scenes. On platforms like YouTube or Facebook, you drag with a mouse or swipe on touchscreens to look around. For the deepest immersion, VR headsets place you right inside the scene. The interaction becomes even more intuitive: users simply look around naturally, and the photo’s perspective responds in real time to head movements, creating a deeply immersive experience that simulates being physically inside the captured environment.
Harnessing 360° Media And Spatial Interactions
360-degree media excels by delivering complete environmental context and giving users control over exploration. It has become standard for virtual real estate tours, allowing buyers to roam properties remotely. Hotels and resorts use it to offer immersive previews. Meanwhile, manufacturers, event planners, and tourism boards leverage it to showcase large spaces, from factory floors to festival grounds.
When combined with spatial computing interactions like annotations, hotspots, and interactive elements, the benefits multiply:
Contextual Information Overlay: Rather than just presenting a scene, spatial computing overlays relevant data, text, images, or even 3D models exactly where they belong within the 360° environment. This deepens understanding without breaking immersion.
Guided Exploration & Navigation: Hotspots serve as interactive guides. Users can actively navigate to points of interest, trigger fresh content, or jump between 360° scenes and external resources.
Actionable Insights & Data Capture: Annotations collect data, solicit feedback, or mark points for follow-up. For example, a quality inspector can note a defect right in the 360° view, linking that insight directly to workflow systems.
Across industries, these capabilities translate into powerful applications:
Manufacturing: Assembly line training becomes interactive and efficient. New employees follow hotspots that highlight tools, parts, and steps within 360° videos enhanced with instructions or voiceovers.
Healthcare: Interactive hospital and clinic tours use hotspots to provide info on departments, patient services, doctors, or wait times. Annotations highlight accessibility features and emergency exits. Patient room setup training allows nurses to learn bed adjustment, equipment placement, and accessibility needs within annotated 360° views.
Security: Patrol route optimization uses 360° videos layered with hotspots marking high-risk areas, restricted zones, or points of interest, supporting training and operational planning with heightened vigilance.
Hospitality: Event planners visualize room setups interactively, annotating seating, stage positions, or décor options, and instantly sharing detailed views with clients. Staff training benefits from virtual navigation through properties, with annotations highlighting key features of rooms, public spaces, and equipment to boost knowledge and service quality.
In sum, 360° media fused with spatial interactions transforms passive viewing into dynamic exploration, embedding information and insight where it matters most. This blend empowers businesses to engage customers, enhance training, streamline operations, and capture actionable data, unlocking strong, measurable value across sectors.
180-Degree Immersive Video: Focused Immersion
180-degree immersive video captures a hemispherical field of view, covering half of a sphere and focusing solely on what lies in front of the camera, rather than a full 360-degree environment. This targeted approach concentrates pixel density where it matters most, delivering sharper, higher-resolution visuals exactly where your attention naturally falls. Instead of capturing everything around, 180-degree video prioritizes quality over quantity, creating a richer, more immersive experience.
Using specialized stereo rigs with dual ultra-wide fisheye lenses, 180-degree video records left- and right-eye views simultaneously without complex stitching. This streamlines lighting and composition while preserving compelling stereoscopic depth.
This format excels when guiding narrative and viewer focus is critical. It offers the depth and immersion of 3D stereoscopy within a wide but focused field of view, ideal for first-person POV experiences like surgical training or equipment repair. It also shines in live event broadcasts, including concerts, sports, and keynote presentations, placing viewers in prime seats and maintaining artistic control.
Affordable DIY rigs under $5,000 make 180-degree immersive storytelling accessible, while high-end setups like Blackmagic’s, costing tens of thousands, push realism to new heights. Red Airship bridges this gap by providing professional capture and processing for ready-to-use immersive content.
Harnessing Immersive 180° Video
Integrating immersive 180° video into existing workflows enhances experiences by adding a focused, high-resolution layer without the complexity of full 360° production. It sharpens what matters most, inviting richer context and deeper sensory connection exactly where user attention naturally rests.
180° video excels at showcasing detailed, depth-rich scenarios such as intricate assembly steps, critical medical procedures, or immersive adventures. Its ability to frame narratives with clarity and presence transforms training, marketing, and communication by zeroing in on key actions and environments.
In manufacturing, 180° video turns complex machinery operation, critical assembly steps, and SOPs into vivid first-person journeys. New employees virtually step into expert roles, seeing operations unfold with realistic depth and focus, improving understanding and retention.
In healthcare, immersive 180° views bring surgical training and patient education to life. Both students and patients gain clarity on complex procedures, reducing anxiety and enhancing comprehension.
On construction sites, 180° immersive videos offer safe yet detailed views of hazards and protocols, focusing attention precisely where needed and creating living safety briefings that boost compliance and awareness.
In hospitality and travel, 180° content lets potential customers experience adventures or life’s key moments with vivid realism, building trust through transparent previews that highlight every detail and ambiance, and helping ease booking decisions.
The real strength of immersive 180° video lies in its ability to focus attention sharply, emotionally engage viewers, and elevate decision-making, delivering business value through compelling, actionable storytelling that integrates seamlessly into existing media landscapes.
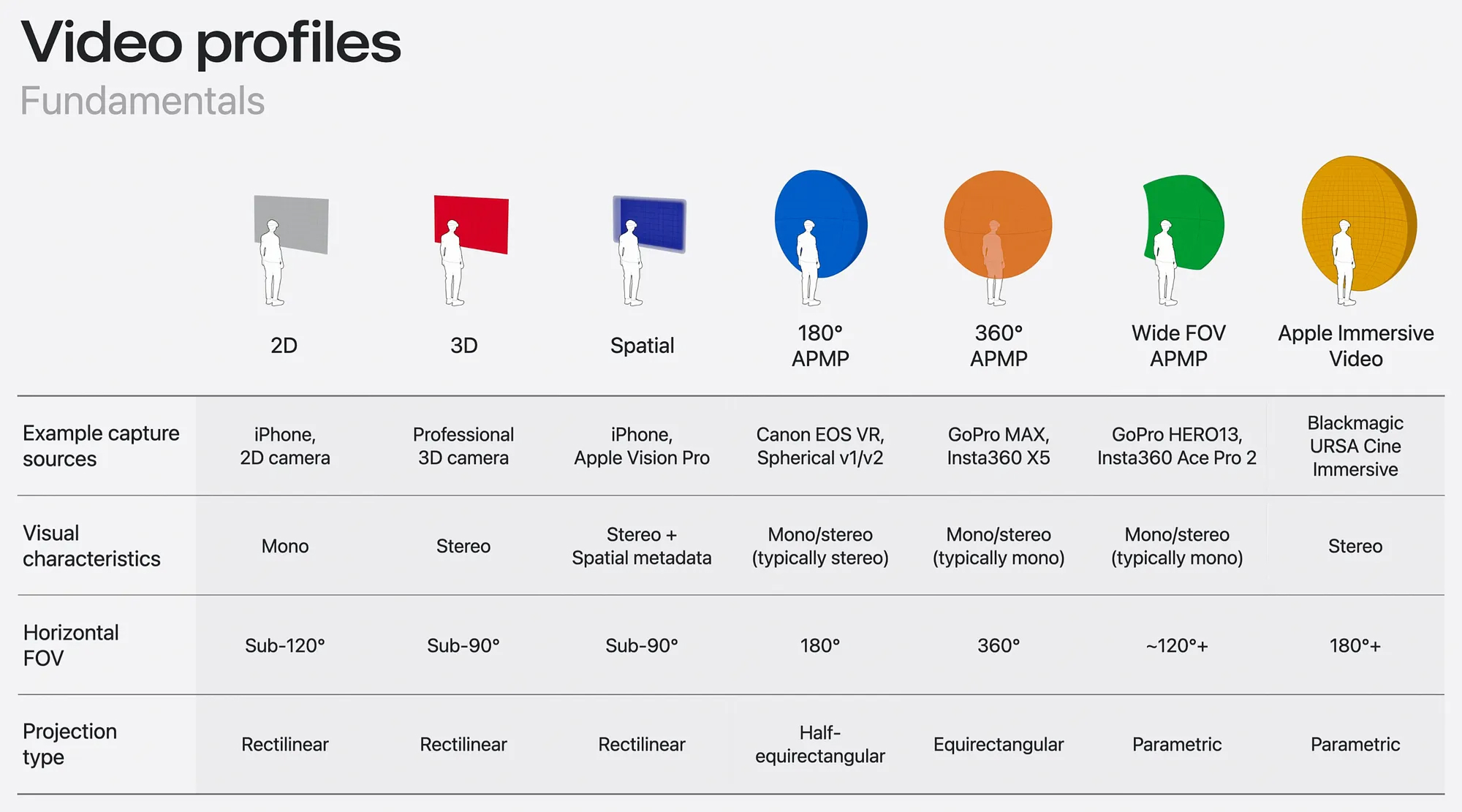
Chart from Apple WWDC
Understanding the investment required for these immersive formats is crucial for strategic adoption. The cost and complexity vary significantly, from a simple capture on a smartphone to professional-grade production.
The lowest barrier to entry is spatial media, especially if your enterprise is already within the Apple ecosystem. With an iPhone 15 Pro or newer, you can capture spatial photos and videos with a device you likely already own. Furthermore, new AI tools are dramatically reducing the cost of converting existing 2D media into spatial formats. This makes it an ideal starting point for businesses looking to add a layer of depth to their content without a major overhaul.
For 360-degree media, the initial investment is higher, as it requires specialized hardware. While professional-grade 360° cameras can cost thousands, affordable consumer models, such as those from Insta360 or GoPro, are available for as little as $350. This makes it a viable option for businesses that need to capture and share full environmental context on a moderate budget.
The most resource-intensive format discussed is 180-degree immersive video. This format prioritizes quality and focused immersion, and the equipment reflects that. While DIY rigs can be assembled for under $5,000, high-end professional setups can run into the tens of thousands of dollars. The investment here is justified by the exceptional depth, clarity, and narrative control it provides, making it suitable for applications where a premium, highly focused experience is critical, such as surgical training or live event broadcasts.
Beyond the Guide: The Future of Spatial Content
While this guide focuses on spatial photos, 360° media, and 180° video, the landscape of immersive content extends even further. 3D assets and photogrammetry content represent the pinnacle of immersive capabilities, offering the highest levels of interaction and visualization. These assets, which can be created from real-world scans or from scratch, are foundational for virtual environments and interactive product models. However, they come with the highest cost and complexity, requiring specialized technical expertise from 3D artists, animators, and developers.
Recognizing the need for accessible entry points, Red Airship works with major spatial computing ecosystem companies to help enterprises navigate this new world. We assist in creating the necessary content assets and developing enterprise apps and programs. Our goal is to provide compelling solutions that solve real-world industry challenges, from training and collaboration to brand communication and product development, ensuring businesses can leverage these powerful new formats effectively.
Resources
Swanson, M. (2024, October 20). Immersive video production tips. Mike Swanson's Blog. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://blog.mikeswanson.com/immersive-video-production-tips/
Apple Inc. (n.d.). Intro to immersive experiences. Apple Support. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://support.apple.com/en-sg/guide/apple-vision-pro/dev7068c3c93/visionos
Paul's notes from watching WWDC2025
